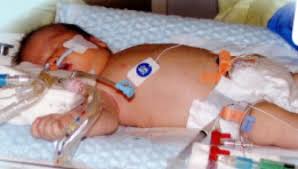
Selective Head and Body Cooling is a therapeutic technique used to treat newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), a condition caused by lack of oxygen and blood flow to the brain at birth. The method involves cooling the baby's head or entire body to reduce brain injury by lowering body temperature, which slows metabolic processes and reduces inflammation.
Selective head and body cooling, also known as therapeutic hypothermia, is a medical treatment primarily used for newborns who have experienced a lack of oxygen at birth, a condition known as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). This therapy involves cooling the infant's body or just the head to a temperature typically between 33.5°C and 34.5°C (92.3°F to 94.1°F) for a duration of 72 hours. The cooling process helps slow the metabolic rate and reduce the risk of brain injury by decreasing inflammation, reducing cell death, and minimizing the release of harmful substances that can damage brain tissue.
The cooling is achieved through specially designed cooling caps for selective head cooling or cooling blankets for body cooling. Continuous monitoring of the infant's temperature, heart rate, and other vital signs is crucial throughout the treatment to ensure safety and effectiveness. Studies have shown that therapeutic hypothermia can significantly improve survival rates and reduce the likelihood of severe neurological disabilities in affected newborns. This intervention has become a standard practice in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) worldwide, demonstrating the importance of early and specialized treatment for vulnerable infants.